
The excess value paid by the purchaser of the shares above the par value can be found in the “Additional Paid-In Capital (APIC)” line item. However, the issuance price of equity typically exceeds the par value, often by a substantial margin. Eliminate annoying banking fees, earn yield on your cash, and operate more efficiently with Rho. Therefore, the stockholder’s equity of Apple Inc. has declined from $134,047 Mn as at September 30, 2017 to $107,147 Mn as at September 29, 2018.
Paid-in capital: Par value of issued stock
Current liabilities are debts typically due for repayment within one year, including accounts payable and taxes payable. Long-term liabilities are obligations that are due for repayment in periods longer than one year, such as bonds payable, leases, and pension obligations. In our modeling exercise, we’ll forecast the shareholders’ equity balance of a hypothetical company for fiscal years 2021 and 2022.
- Overall, this article provides readers with a detailed definition of stockholders’ equity along with the most common misconceptions about the value.
- Unlike public corporations, private companies do not need to report financials nor disclose financial statements.
- Consider this carefully if you’re seeking equity instead of debt financing.
- Once all liabilities are taken care of in the hypothetical liquidation, the residual value, or “book value of equity,” represents the remaining proceeds that could be distributed among shareholders.
What does shareholders’ equity tell you about a company?
In 2021, the share repurchases are assumed to be $5,000, which will be subtracted from the beginning balance. Earlier, we were provided with the beginning of period balance of $500,000. But an important distinction is that the decline in equity value occurs due to the “book value of equity”, rather than the market value.
Paid-in Capital
Over the years, shareholders’ equity has become a fundamental component of a company’s balance sheet, offering insight into its financial well-being. Since repurchased shares can no longer trade in the markets, treasury stock must be deducted from shareholders’ equity. Enter the value of all assets and liabilities owned by shareholders to determine the shareholder’s equity. Negative shareholders’ equity suggests that the company might want to consider reducing its liabilities or finding ways to boost its profits.
Why is it important for a company to have enough stockholders’ equity?
It can be calculated using the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) or the dividend capitalization model (DCM). Either way, the CoE factors in, along with the cost of debt, when calculating your weighted average cost of capital (WACC). Be sure to study these concepts if you’re planning on doing a round of fundraising. It’s a risk factor calculated by comparing the company’s rate of return with the average market rate of return (MRR).
Everything You Need To Master Financial Modeling
In these types of scenarios, the management team’s decision to add more to its cash reserves causes its cash balance to accumulate. If we rearrange the balance sheet equation, we’re left with the shareholders’ equity formula. The equity risk premium is the difference between the risk-free rate and the average market rate of return. That “margin” factors into the decision-making for stock market and equity investments.
If this figure is negative, it may indicate an oncoming bankruptcy for that business, particularly if there exists a large debt liability as well. This calculator streamlines the process of determining shareholders’ equity, making it accessible for stakeholders to assess a company’s financial position quickly. Another benefit of share buybacks is that such corporate actions can send a positive signal to the market, much like dividends, without the obligation to maintain the repurchases (e.g. a one-time repurchase). Once all liabilities are taken care of in the hypothetical liquidation, the residual value, or “book value of equity,” represents the remaining proceeds that could be distributed among shareholders. Transactions that involve stockholders are primarily the distribution of dividends and the sale or repurchase of the company’s stock. Long-term liabilities are obligations that are due for repayment over periods longer than one year.
The equity capital/stockholders’ equity can also be viewed as a company’s net assets. You can calculate this by subtracting the total assets from the total liabilities. Shareholders’ equity, often referred to as stockholders’ equity, is a crucial financial metric in accounting, representing the residual interest in the assets of a corporation after deducting its liabilities. It provides a snapshot of a company’s financial health and stability, crucial for investors, creditors, and the company’s management. By comparing total equity to total assets belonging to a company, the shareholders equity ratio is thus a measure of the proportion of a company’s asset base financed via equity. It is calculated by subtracting the total liabilities from the total assets.
As per the publicly released financial data, the following information is available. A company’s assets and liabilities can change at any time as well due to unforeseen circumstances. Current assets are those that can be converted to cash within a year such as accounts receivable and inventory. Long-term assets are those that can’t be converted to cash or consumed within a year such as real estate properties, manufacturing plants, equipment, and intangible items like patents. Cash takes up a large portion of the balance sheet, but cash is actually not considered an asset because it is expected that cash will be spent soon after it comes into the business. One common misconception about stockholders’ equity is that it reflects cash resources available to the company.
Market analysts and investors prefer a balance between the amount of retained earnings that a company pays out to investors in the form of dividends and the amount retained to reinvest into the company. Share capital is the money a company raises by selling its shares to shareholders in exchange for cash. Rather, they only list those accounts that are relevant to their situation.
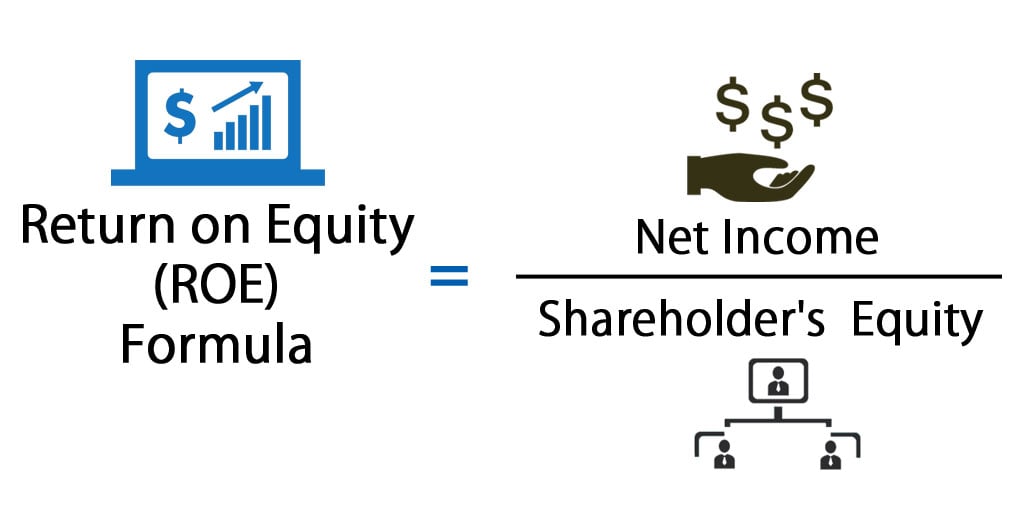
To calculate stockholders’ equity, you can use one of two accounting equations. The retained earnings portion reflects the percentage of net earnings that were not paid to shareholders as dividends and should not what is irs form w be confused with cash or other liquid assets. The number of shares issued and outstanding is a more relevant measure than shareholder equity for certain purposes, such as dividends and earnings per share (EPS).
